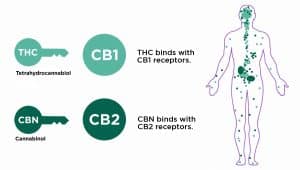
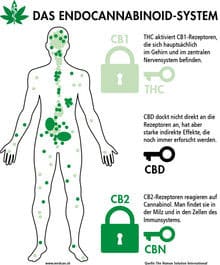
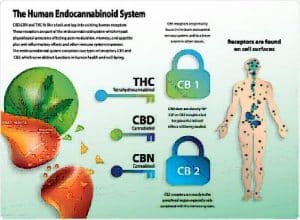
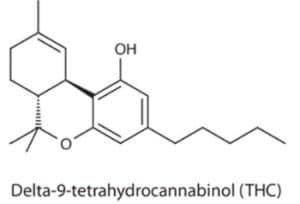
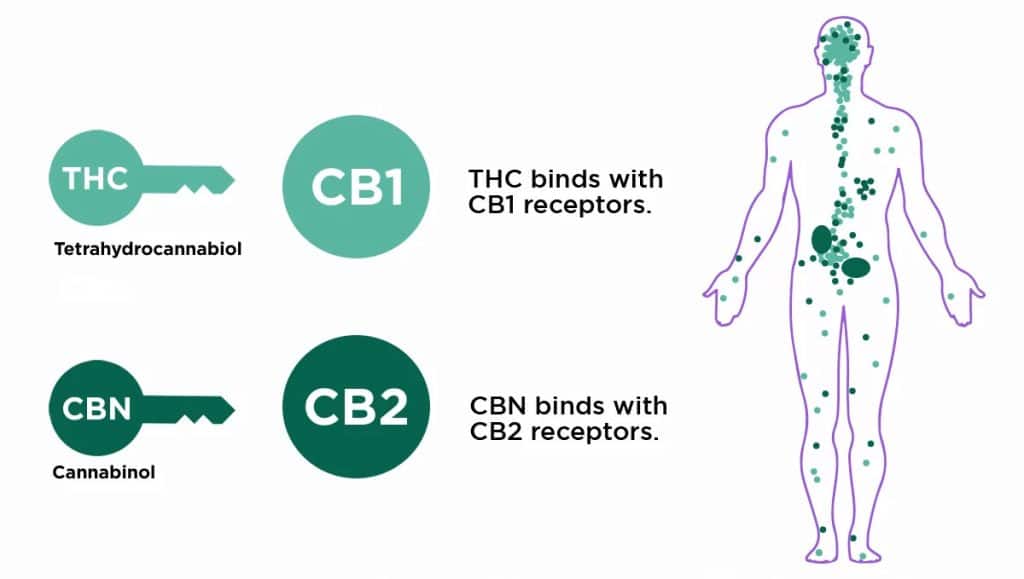
Δ 9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ 9 -THC), which was first isolated and identified in 1964, led to the creation of a separate class of compounds called cannabinoids. H Δ 9 -THC which acts protectively for the plant, is the main psychoactive substance, the most powerful and pharmacologically active and acts on the receptors of the endocannabinoid system (CB1, CB2). CB1 receptors are present in the Central Nervous System and in various peripheral tissues and CB2 receptors in various peripheral tissues but mainly in immune cells. Tetrahydrocannabinol, a phytocannabinoid, attaches to, blocks, and modulates these receptors, just as the endocannabinoids produced by
our body and act as messengers. Specifically, THC exhibits absolute affinity for CB1 receptors.
Based on the Greek legislation L. 4801/2021 (Government Gazette 83/A/24-05-2021), which concerns finished products of medicinal cannabis, the THC content refers to a limit > 0.2%. Besides Δ 9 -THC, other characteristic cannabinoids are cannabidiol
(CBD) and cannabinol (CBN). At least 100 cannabinoids are known today.